Introduction:
Social Security Numbers (SSNs) play a crucial role in the identity verification process in many countries, most notably in the United States. Originally introduced as a part of the Social Security Act in 1935, SSNs were primarily designed to track individuals’ earnings and determine their eligibility for Social Security fullz info. Over time, these nine-digit numbers have become a ubiquitous and essential component of various aspects of daily life, including financial transactions, employment, and government services.
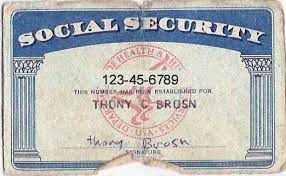
The Structure of Social Security Numbers:
A standard Social Security Number follows the format XXX-XX-XXXX, where each X represents a digit. The first three digits, known as the Area Number, indicate the state where the individual applied for their SSN. The next two digits, the Group Number, have no specific meaning but were originally intended to aid in the manual filing of records. The final four digits, the Serial Number, are assigned sequentially and uniquely identify each individual within a particular group.
Importance of Social Security Numbers:
- Government Benefits and Services:
SSNs are pivotal in determining eligibility for various government benefits and services, such as Social Security retirement benefits, Medicare, and unemployment benefits. They serve as a key identifier for individuals seeking assistance from government programs. - Employment and Taxation:
Employers use SSNs to report employee earnings to the government and to verify employees’ eligibility to work in the country. Additionally, SSNs are essential for filing income taxes, tracking contributions to Social Security, and facilitating tax refunds. - Financial Transactions:
SSNs are often required for financial transactions, including opening bank accounts, applying for credit cards, and securing loans. Financial institutions use these numbers to assess creditworthiness and prevent identity theft. - Education and Healthcare:
Educational institutions may request SSNs for enrollment and financial aid purposes. Similarly, healthcare providers often use SSNs for billing and insurance claims.
Security Concerns and Identity Theft:
The widespread use of SSNs makes them an attractive target for identity thieves. Unauthorized access to an individual’s SSN can lead to various forms of identity theft, such as financial fraud, opening fraudulent accounts, and unauthorized access to personal information.
To mitigate these risks, individuals are advised to:
- Safeguard Personal Information:
Never share SSNs or other sensitive information over insecure channels, such as unencrypted emails or public Wi-Fi networks. - Regularly Monitor Accounts:
Keep a close eye on bank statements, credit reports, and other financial accounts to detect and report any suspicious activity promptly. - Use Secure Websites:
When providing SSNs online, ensure that the website is secure (https://) and reputable. Avoid sharing sensitive information on unfamiliar or unsecured platforms. - Secure Physical Documents:
Store documents containing SSNs, such as Social Security cards, in a secure and locked location to prevent physical theft.
Conclusion:
While Social Security Numbers are vital for various aspects of modern life, their importance comes with the responsibility of safeguarding them. Awareness of the potential risks and adopting secure practices can help individuals protect their identities and maintain the integrity of this essential identifier in the digital age. Government agencies, businesses, and individuals all play a role in ensuring the responsible use and protection of Social Security Numbers to build a more secure and trustworthy society.